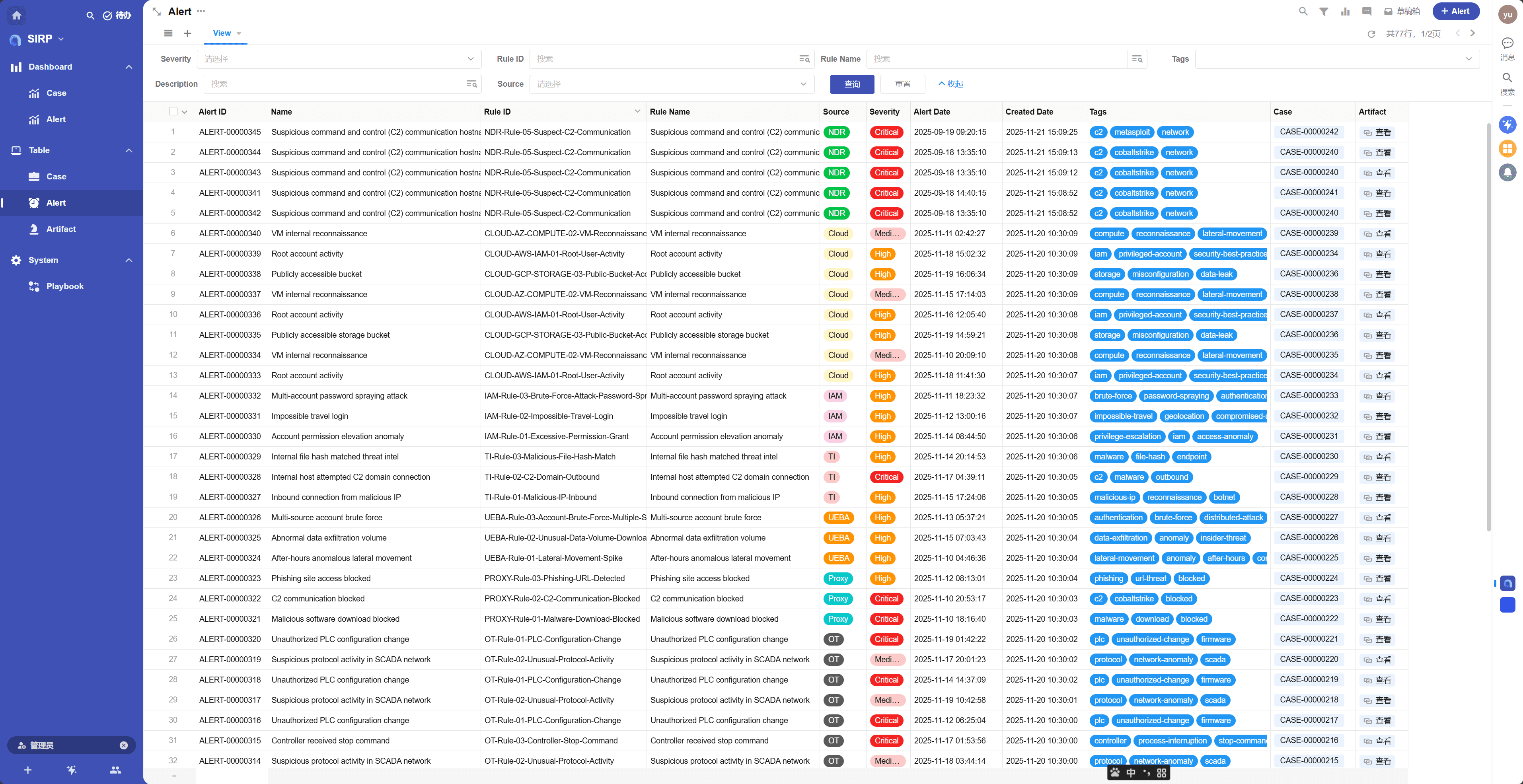
Alert
- Centralized display of all alert records.
- All fields in alerts are read-only by default and cannot be edited.
- Analysts do not modify alert data; they only conduct investigations and response work based on alert data.
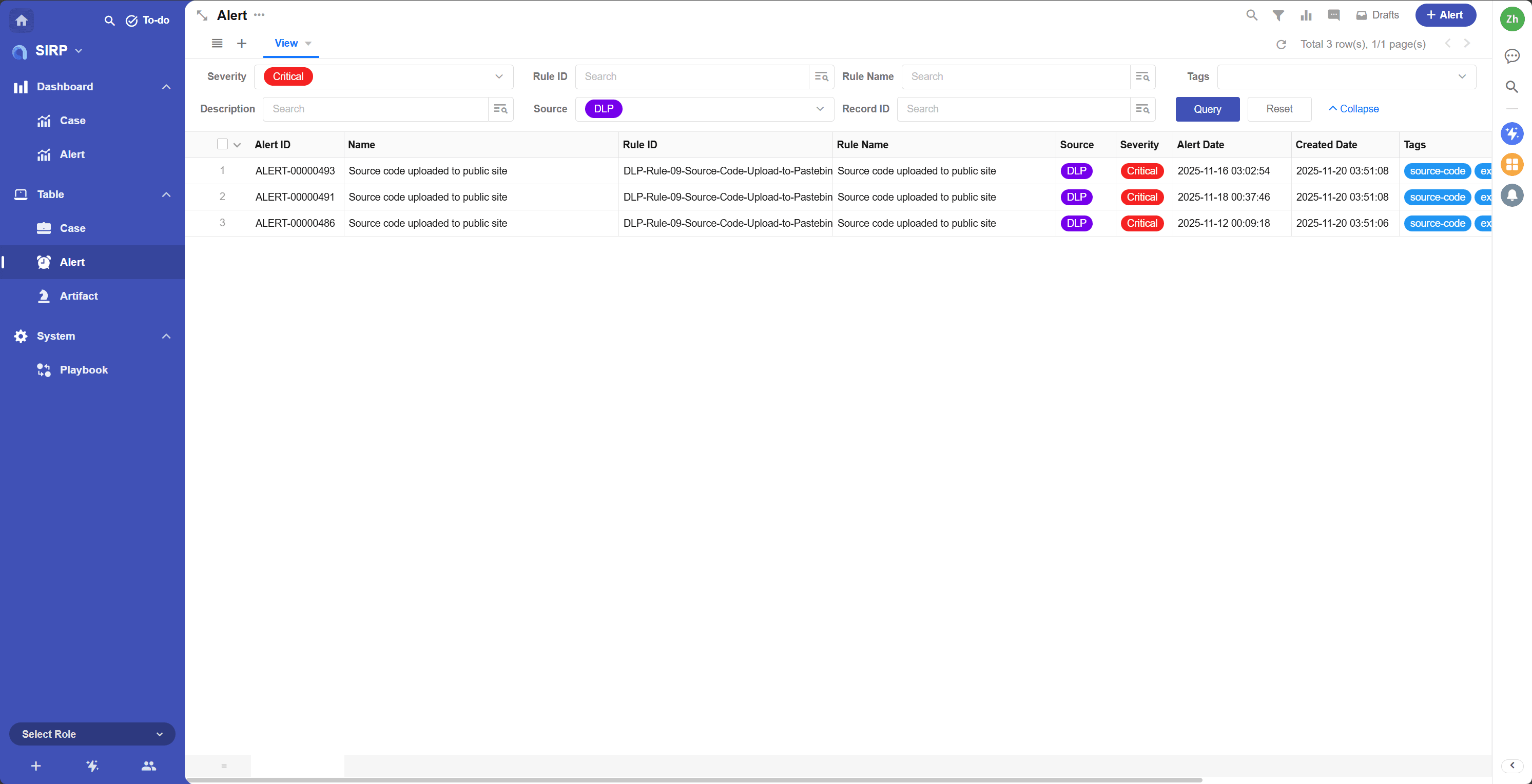
View
Supports multiple filtering and sorting functions.
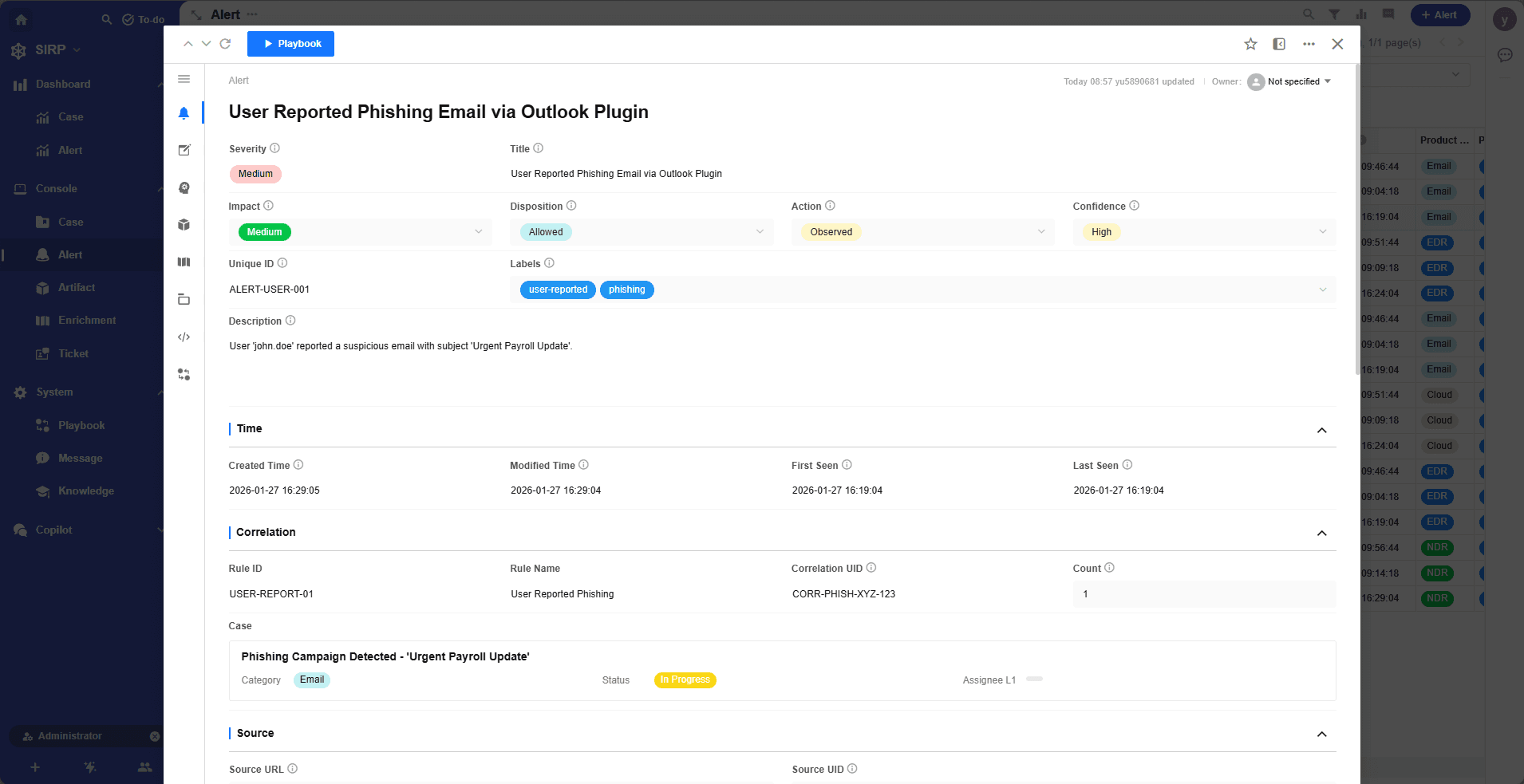
Detail
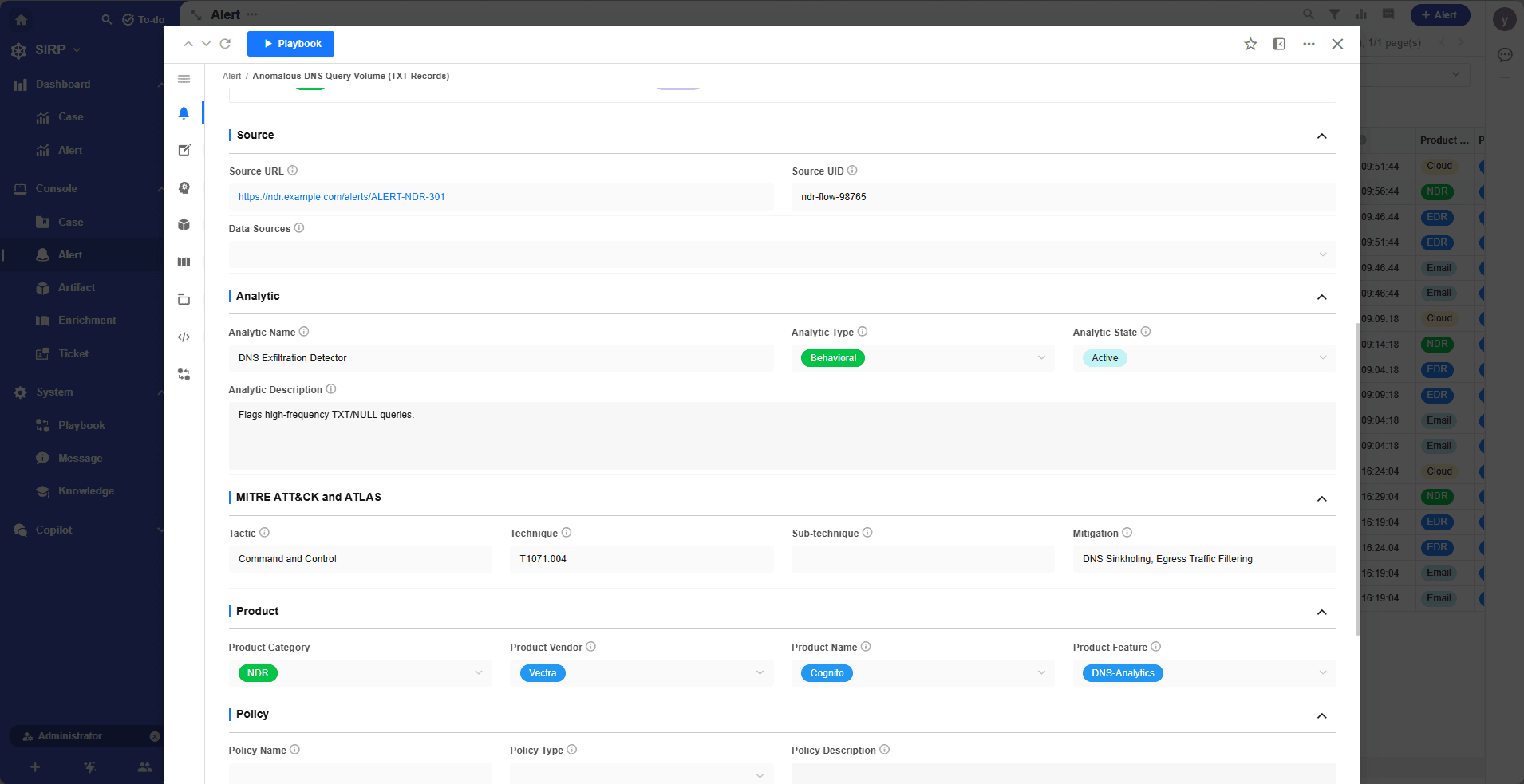
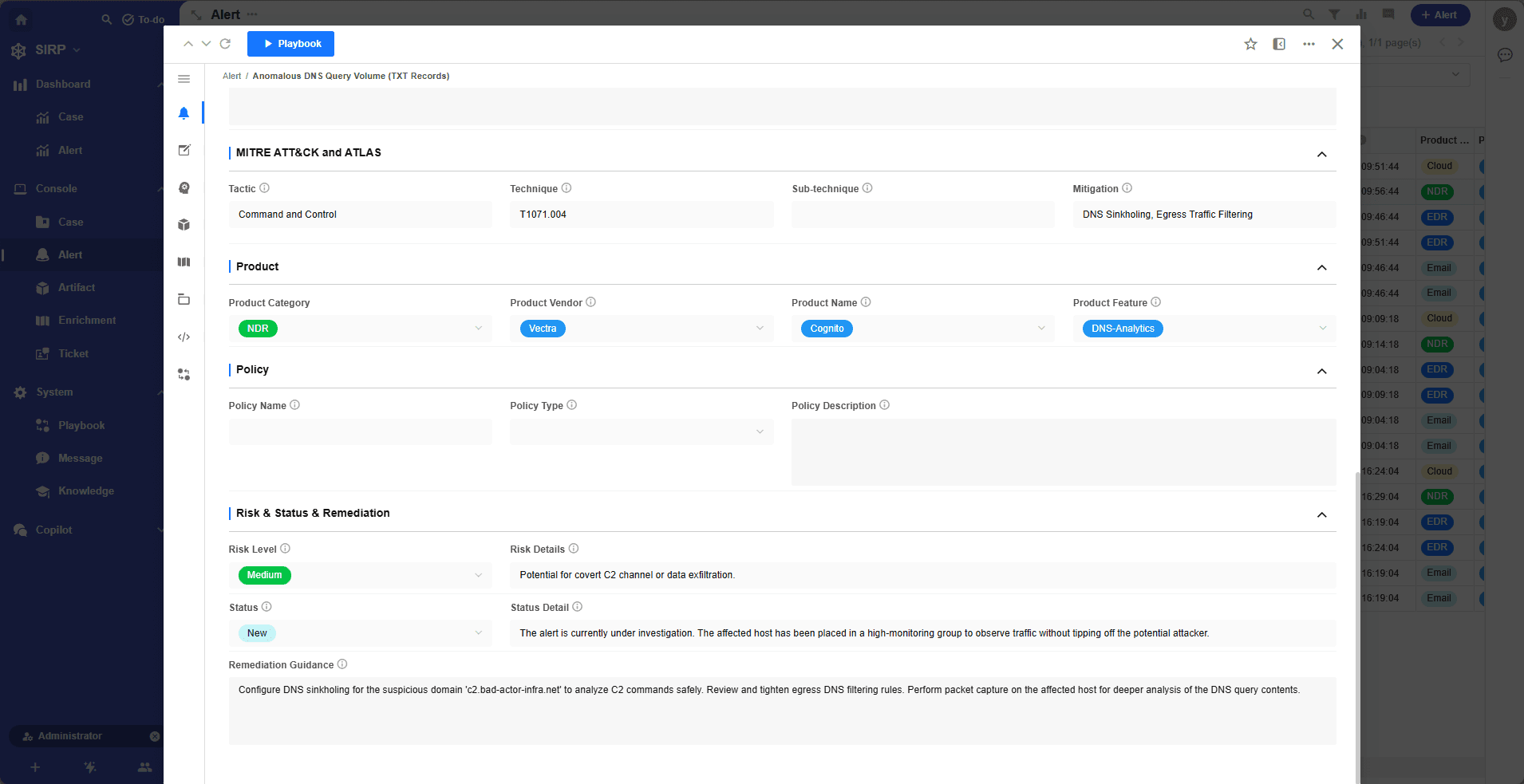
Alert Operations Panel
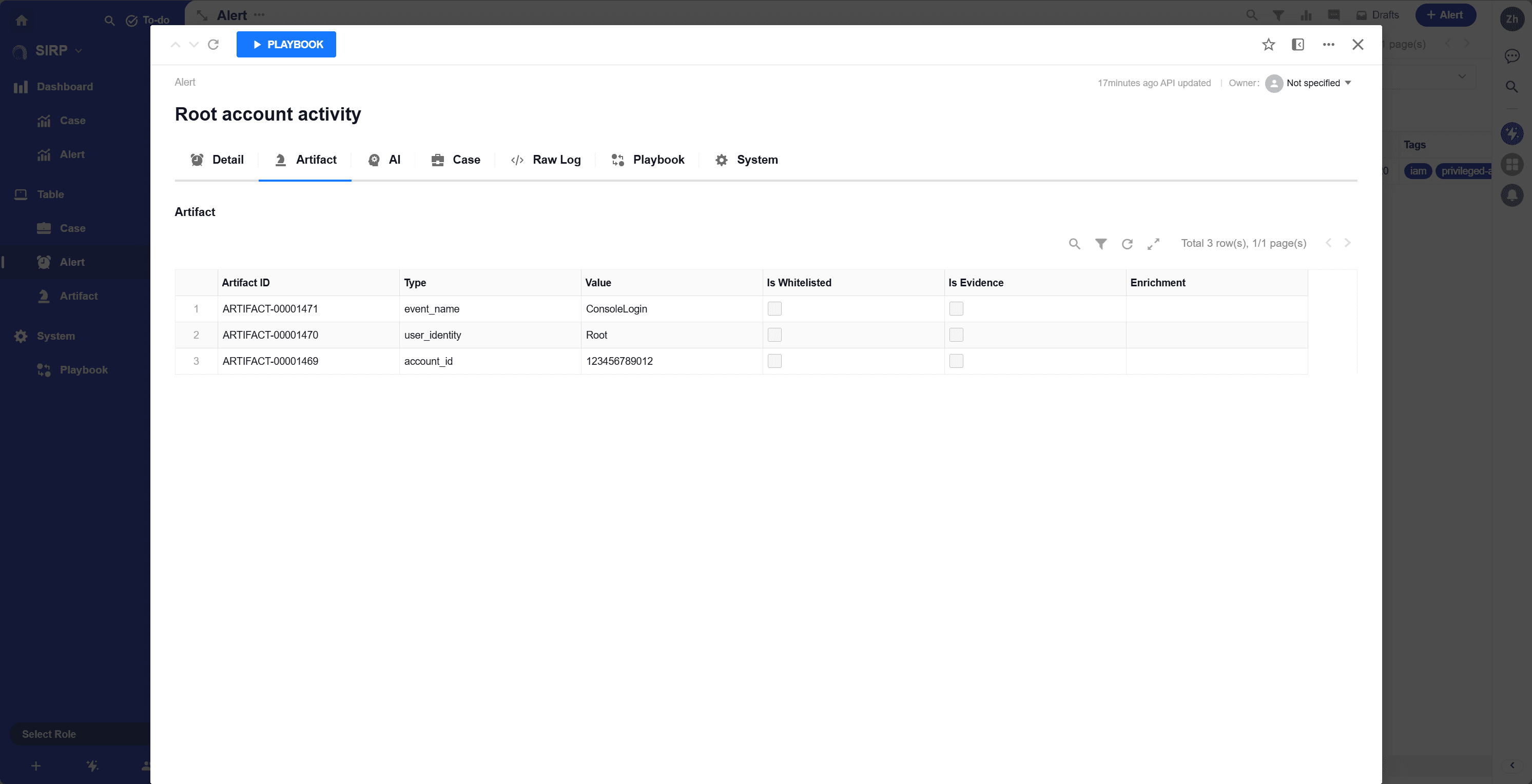
Artifact
List of artifacts related to the alert.
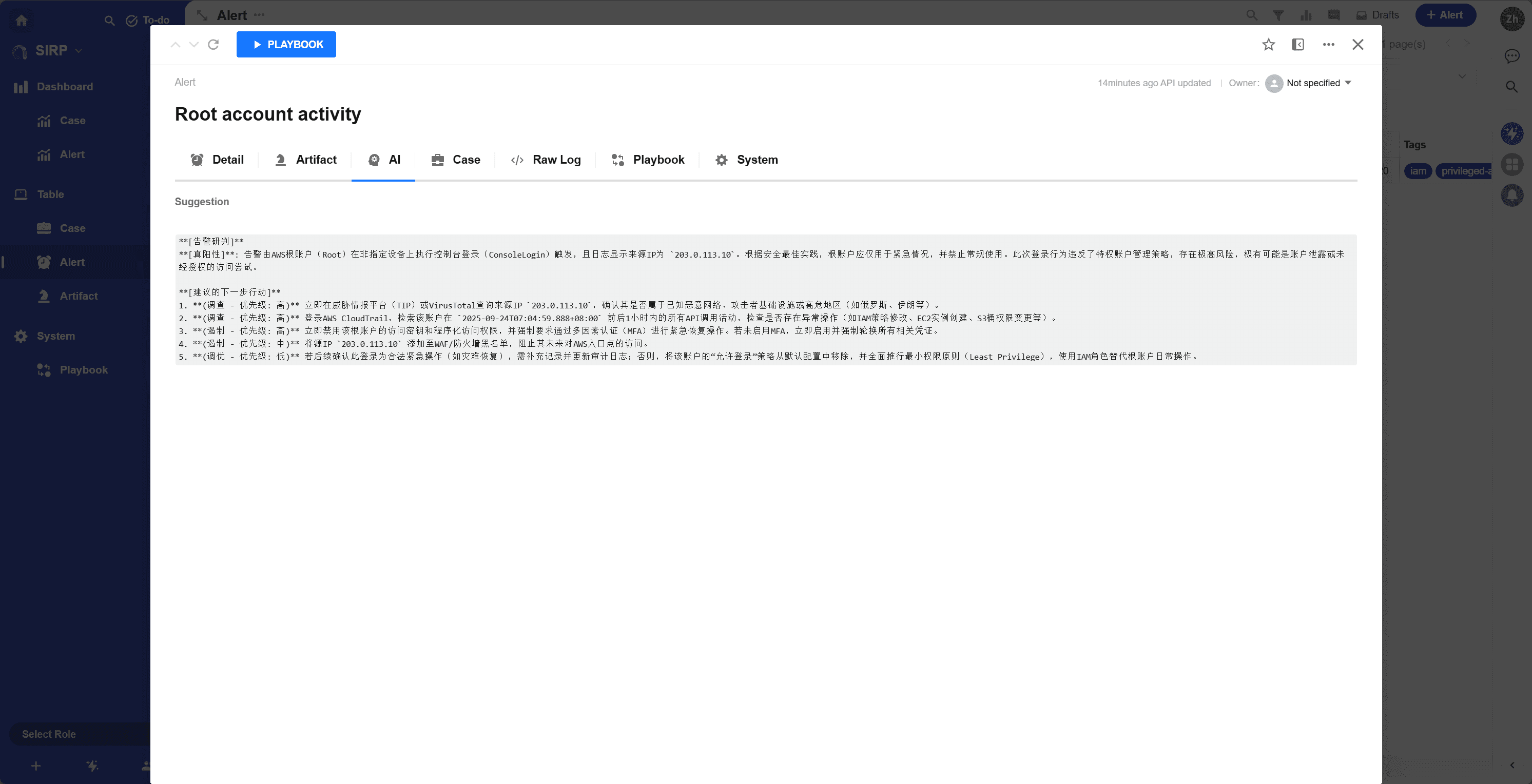
AI
AI analysis results generated based on alert content.
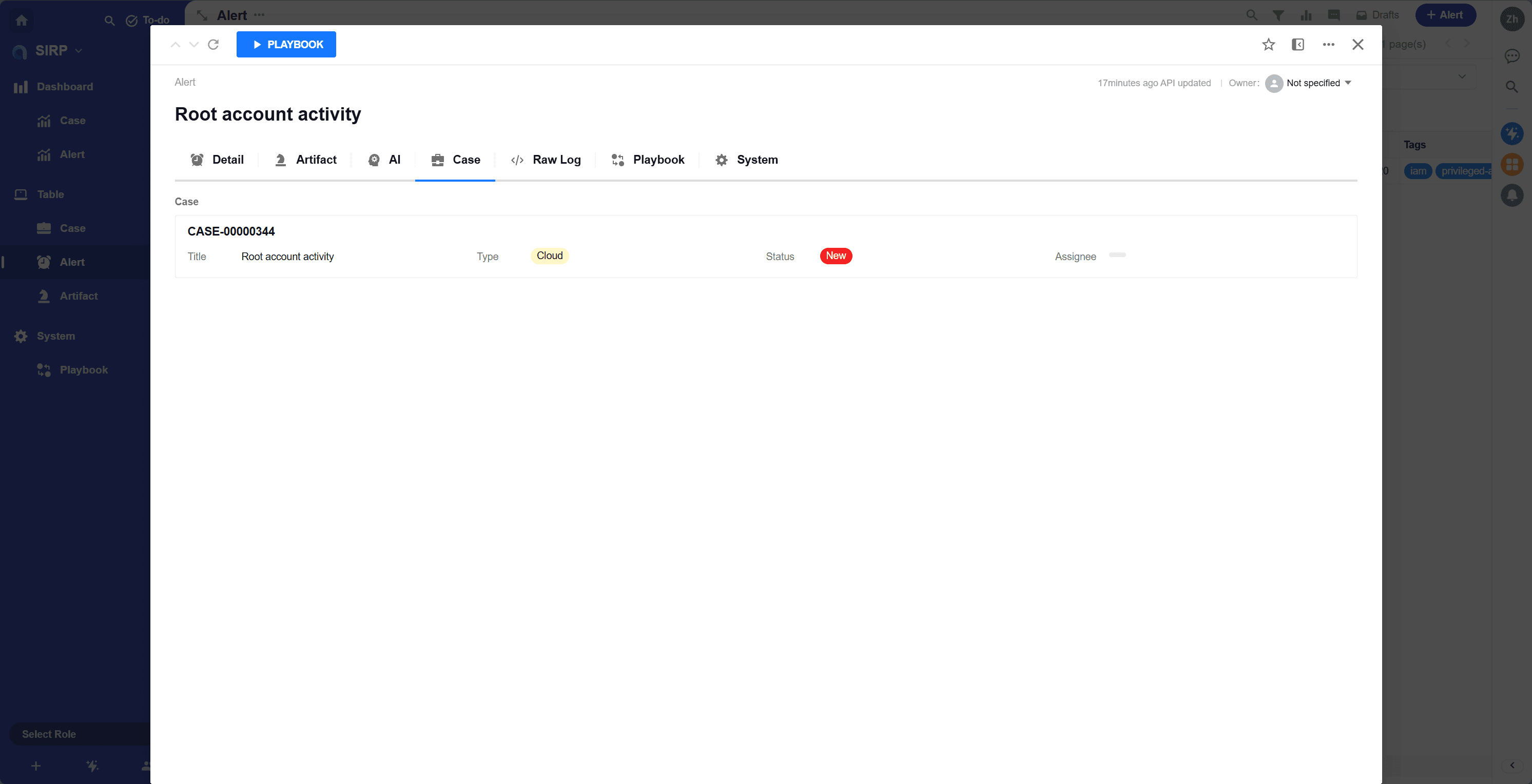
Case
Cases associated with the alert.
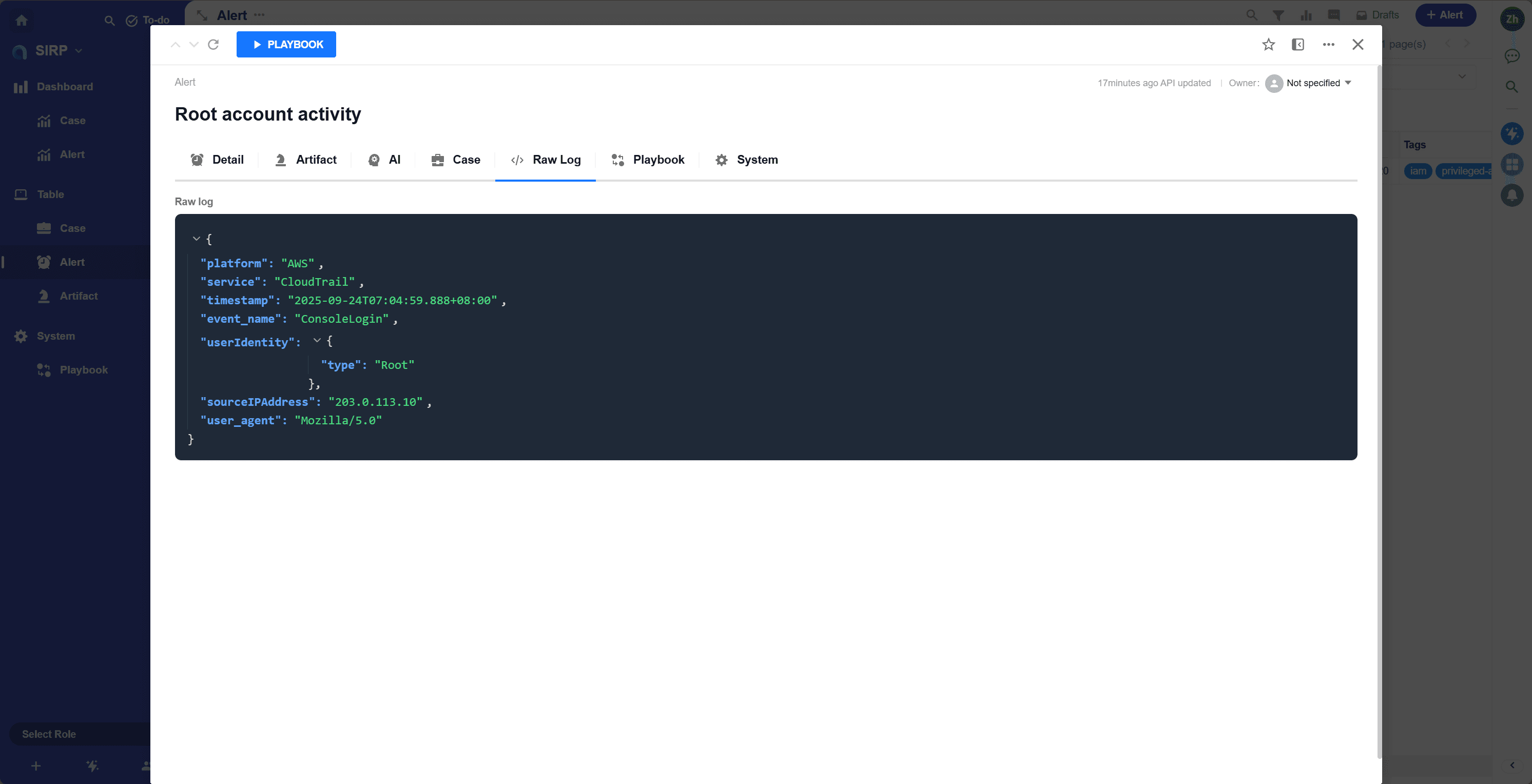
Raw Log
Original log content of the alert. JSON format.
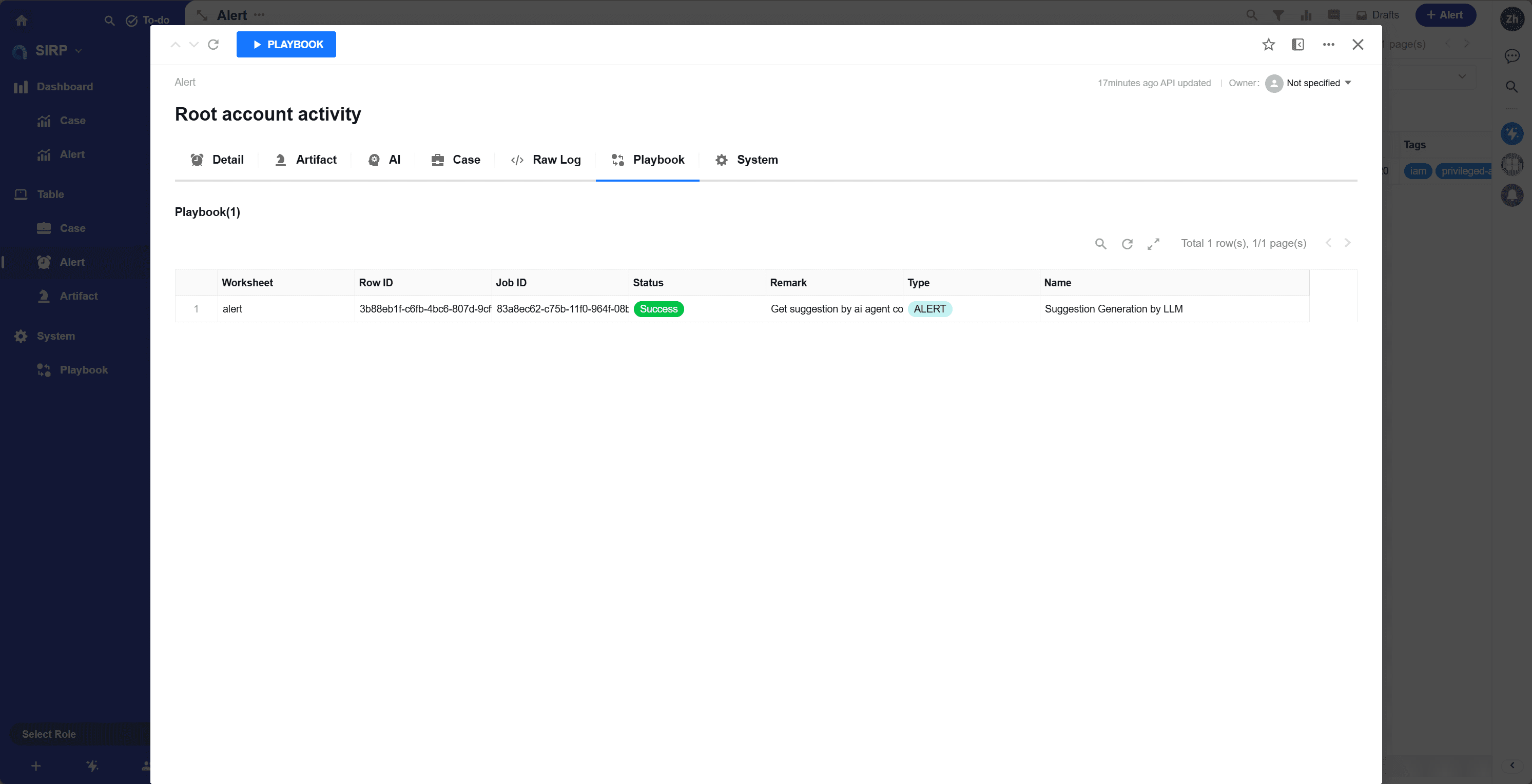
Playbook
Playbook execution history related to the alert.
System
System fields of the alert.